Getting multiple AIs to work together is the next frontier.
Agent Orchestration is the coordination and management of multiple AI agents working together to accomplish complex tasks that would be difficult for a single agent to handle alone.
Think of it like conducting an orchestra.
Each musician is a specialized AI agent.
One plays the violin (researches data).
Another plays the cello (analyzes sentiment).
Another plays the flute (writes a summary).
They are all masters of their instrument.
But without a conductor—the orchestration layer—you just get noise.
The conductor ensures they all play in harmony, at the right time, to create a beautiful symphony, or in this case, to solve a complex problem.
Getting this right means moving from single-tool AI to building truly autonomous systems that can tackle multi-step, dynamic challenges. Ignoring it means hitting a hard ceiling on what AI can achieve.
***
What is Agent Orchestration?
It’s the art and science of making a team of specialized AI agents collaborate effectively.
Instead of building one massive, monolithic AI that tries to do everything…
You build a team of smaller, expert agents.
Each agent has a specific skill.
- A research agent.
- A data analysis agent.
- A coding agent.
- A quality assurance agent.
The orchestration layer acts as the project manager.
It breaks down a complex request, like “Analyze our competitor’s latest earnings report and draft a response for our marketing team.”
It assigns the sub-tasks to the right agent.
It manages the flow of information between them.
And it pieces together their individual contributions into a final, coherent output.
How does Agent Orchestration differ from traditional automation?
The key difference is dynamism versus rigidity.
Traditional workflow automation is like a factory assembly line.
Each step is predefined.
The process follows a fixed, unchangeable path.
If Step A is done, do Step B, then Step C.
There’s no room for deviation.
Agent Orchestration is like an expert consulting team.
The “consultants” (agents) can make decisions and adapt in real-time.
The orchestration layer might give a task to the research agent.
Based on what the researcher finds, the plan might change entirely.
Maybe the analysis agent is no longer needed, and instead, a legal review agent must be brought in.
It’s an adaptive, intelligent workflow, not a static one.
It also differs from:
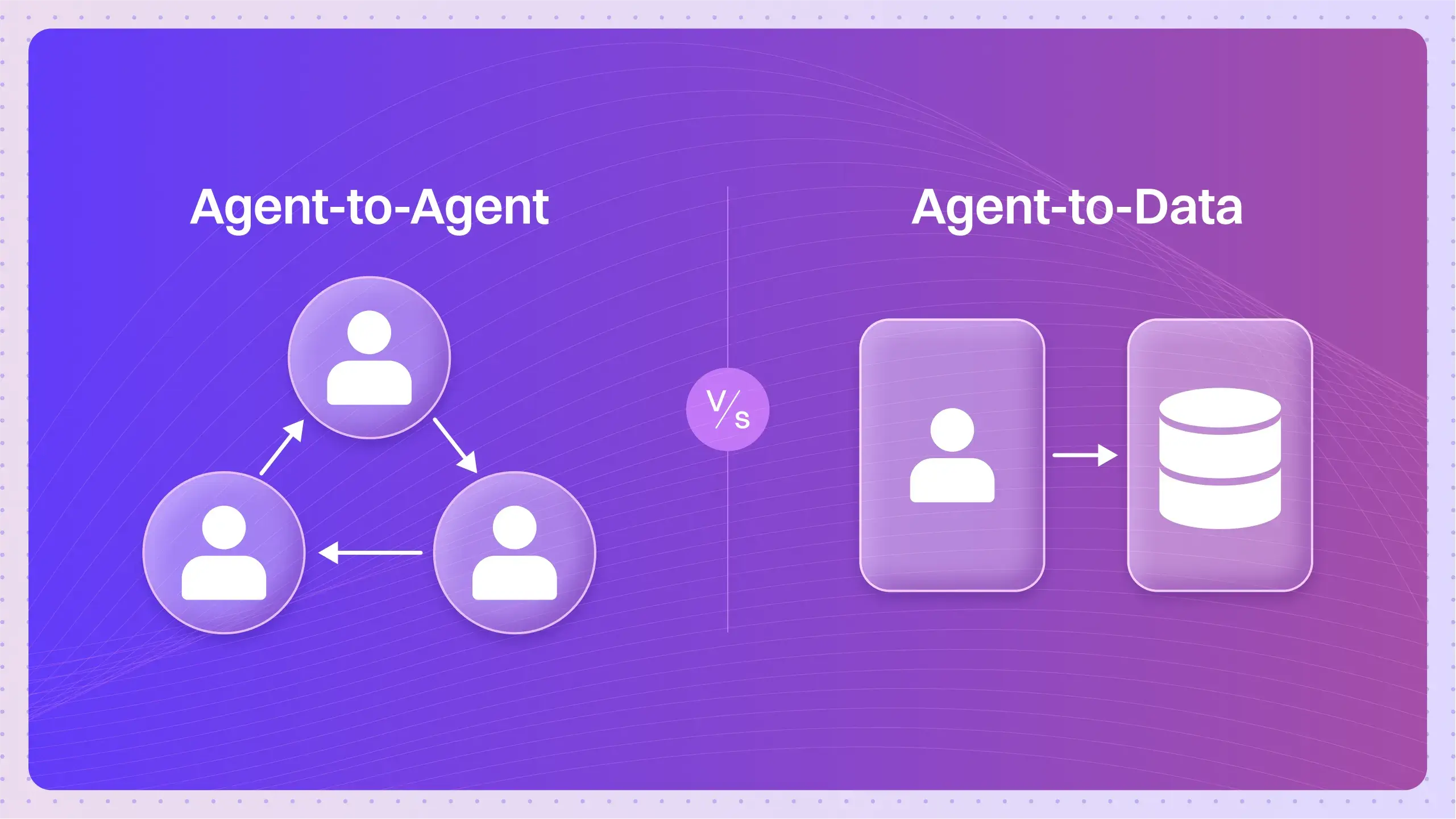
- Multi-Agent Systems: These can be loosely coupled, with agents acting more independently. Orchestration implies a more structured, managed coordination with clear communication protocols.
- Human-in-the-Loop Systems: While orchestration can include human oversight, the goal is often to create autonomous systems that can operate without constant human intervention, unlike systems that rely on humans for key decisions.
What are the key components of an Agent Orchestration system?
A well-functioning orchestration system has several core parts.
The Orchestrator (The Conductor)
This is the central controller. It’s the brain of the operation that decomposes tasks, routes them to the appropriate agents, and manages the overall state of the workflow.
The Agents (The Musicians)
These are the specialized AI models or functions. Each one is an expert at a specific task, like web scraping, data validation, code generation, or natural language summarization.
Communication Channels (The Sheet Music)
This is the protocol for how agents talk to each other and to the orchestrator. It’s a structured way to pass information, results, and instructions back and forth, often using message passing interfaces or APIs.
State Management (The System’s Memory)
This component keeps track of the entire process. What tasks are done? What were the results? What needs to happen next? It ensures context isn’t lost as the workflow moves from one agent to another.
What benefits does Agent Orchestration provide for complex AI systems?
It unlocks solutions to problems that a single agent simply can’t handle.
- Specialization and Expertise: You get to use the best tool for each job. A coding agent writes code, and a writing agent refines prose. This leads to higher-quality outputs.
- Modularity and Scalability: It’s easier to maintain and upgrade. If a better analysis agent comes along, you can swap it in without rebuilding the entire system. Need more power? Add more agents to work in parallel.
- Resilience and Fault Tolerance: If one agent fails, the system doesn’t have to crash. The orchestrator can retry the task, assign it to a different agent, or flag the issue for human review.
- Tackling Complexity: It allows AI to perform long, multi-step reasoning and execution chains that would otherwise fail or lose context.
What challenges exist in implementing effective Agent Orchestration?
It’s not as simple as just connecting a few APIs.
The complexity can be a major hurdle.
Debugging a system where five different AIs are interacting is tough.
Where did it go wrong? Was it the research agent’s data? The analyst’s logic? Or the orchestrator’s instructions?
Other common challenges include:
- Communication Bottlenecks: Ensuring agents can pass large amounts of information between each other efficiently without creating delays.
- State Management: Keeping a consistent and accurate state across the entire workflow, especially for long-running tasks.
- Error Handling: Building robust recovery paths for when agents fail, produce hallucinations, or return unexpected results.
- Cost Management: Running multiple powerful AI agents can get expensive quickly. Effective orchestration involves optimizing which agents are called and when.
What frameworks are available for Agent Orchestration?
You don’t have to build everything from scratch.
The core isn’t about general coding, it’s about robust evaluation and state management harnesses.
Frameworks like LangGraph and CrewAI are specifically designed for this. They provide tools to define agents and structure them into cyclical graphs or collaborative crews.
This allows developers to build stateful, multi-agent applications where agents can work together, pass information, and even call other agents for help.
At a lower level, the concept relies on mechanisms like:
- Planning-Execution-Reflection Loops: A cognitive cycle where agents plan their actions, execute them, and then reflect on the outcome to improve their next steps.
- Message Passing Interfaces (MPI): Standardized communication protocols that create a common language for agents to exchange data and instructions in a structured way.
Quick Test: Spot the better design
You need an AI system to plan a marketing campaign for a new product launch. Which approach uses orchestration effectively?
A. A single, giant AI model is prompted with “Plan the entire marketing campaign.”
B. A researcher agent gathers market data, a strategist agent defines the target audience, a content agent drafts ad copy, and a scheduler agent plans the post timeline.
C. A simple script that just posts “New Product!” on social media every day.
(The answer is B. It breaks the complex task into specialized roles, which is the core principle of Agent Orchestration.)
How is Agent Orchestration being used in real-world applications?
It’s already powering some of the most advanced AI you use.
- Lyzr: Our own platform at Lyzr enables businesses to create powerful workflows by orchestrating specialized agents. This allows for complex data processing, analysis, and reporting tasks to be automated reliably.
- OpenAI: GPT-4’s advanced reasoning isn’t magic. It relies on internal orchestration to manage chain-of-thought, self-correction, and other processes to break down and solve difficult problems.
- Anthropic: Claude Opus uses a similar internal orchestration method. It breaks down complex reasoning tasks into smaller sub-problems and assigns them to specialized internal modules to arrive at a more accurate answer.
***
Deeper Questions on Agent Orchestration
How does communication work between agents in an orchestrated system?
Typically through APIs or a centralized message queue. The orchestrator sends a task (e.g., a JSON object with instructions and data) to an agent’s endpoint. The agent processes it and returns its output in a structured format.
What role does memory play in Agent Orchestration?
It’s critical. The system needs both short-term memory (what happened in the last step?) and long-term memory (what have we learned from previous runs?). This context is stored in a state management system, often a vector database or a key-value store, allowing agents to make informed decisions.
Can Agent Orchestration improve the reliability of AI systems?
Yes, significantly. By breaking tasks down, you reduce the chance of a single agent failing a large, complex job. If one agent fails, the orchestrator can implement fallbacks or retries, making the overall system much more robust than a single monolithic model.
How does Agent Orchestration handle error recovery?
Good orchestration includes built-in error handling. This can involve automatic retries, switching to a backup agent or model, or escalating the failure to a human operator with a full report of what went wrong and where.
What security considerations are important for Agent Orchestration?
Each agent should operate with the principle of least privilege, meaning it only has access to the tools and data absolutely necessary for its job. Sandboxing agents to prevent them from interfering with each other or accessing sensitive system resources is also crucial.
How can Agent Orchestration be monitored and debugged?
Through comprehensive logging and tracing. Tools like LangSmith or custom dashboards are used to visualize the entire workflow, showing the inputs and outputs of each agent at every step. This makes it possible to pinpoint the source of errors or inefficiencies.
What is the relationship between Agent Orchestration and LLM reasoning?
Orchestration is the framework that directs an LLM’s reasoning abilities. Instead of asking an LLM to “think” about a whole problem at once, orchestration guides it through a series of smaller, more manageable reasoning steps, often using different specialized agents for each step.
How does Agent Orchestration scale with increasing task complexity?
It scales remarkably well. For more complex tasks, you can add more specialized agents to the team or create hierarchical structures where one orchestrator manages several sub-orchestrators, each responsible for a different part of the problem.
What is the future direction of Agent Orchestration technologies?
The future is more autonomy. We’re moving toward systems where orchestrators can dynamically assemble their own teams of agents based on a given task, and where agents can learn and improve their collaborative skills over time.
How do you evaluate the effectiveness of an Agent Orchestration system?
Evaluation is multi-faceted. Key metrics include task completion rate, the final quality of the output, overall latency (how long it takes), the computational cost, and the system’s robustness in handling errors and edge cases.
***
The future isn’t about finding the one perfect AI model. It’s about building the perfect AI team. Agent Orchestration is the playbook that will make that collaboration possible.
Did I miss a crucial point? Have a better analogy to make this stick? Let me know.