Table of Contents
ToggleAI systems generally fall into two categories: agentic and non-agentic.
Agentic systems possess autonomy, make independent decisions & perform complex tasks without human intervention. Think autonomous driverless cars.
In contrast, non-agentic systems operate within predefined parameters, & require explicit instructions for each task. Think cars with drivers with maps.
In this article we are going to dig deep & look at the differences in architecture, workflows, UI, scalability between agentic & non-agentic workflows while providing industry & functional specific examples across banking, healthcare, transportation, customer support and sales.
Lots to cover. So let’s dive in.
How Systems Have Evolved to Do More for Users?
Non-agentic AI systems require users to provide direct instructions for every task, acting as responsive tools. In contrast, agentic AI systems take the initiative by understanding context, making decisions, and acting independently when needed.
This shift is redefining how we interact with technology, making it more proactive and collaborative.
| Aspect | Agentic Systems | Non-Agentic Systems |
| Interface Type | Transition from traditional GUIs to human-AI interfaces capable of understanding natural language. | Depend on static GUIs requiring manual navigation and input. |
| User Interaction | Enable intuitive interactions, reducing the learning curve and improving accessibility. | Can become cumbersome, especially when dealing with complex tasks or multiple systems. |
| Customization | Generate contextual interfaces on-the-fly, tailored to user needs. | Limited customization options, often leading to user frustration. |
| Interaction | Example Agentic System: A voice-activated smart home system that understands natural language commands to control devices. | Non-Agentic System: A traditional remote control requiring button presses for each function. |
What is an Agentic System?
If you’re not technical, think of an agentic system as something that doesn’t wait for step-by-step instructions. You give it a goal, and it figures out the steps, makes decisions, and gets it done, like a smart assistant that knows what to do without constant direction.
Now, if you’re a tech person: an agentic system combines perception, reasoning, and autonomous decision-making. It handles multi-step tasks, invokes APIs or tools when needed, maintains context, and dynamically adapts to changing inputs, all without human-in-the-loop prompts at each step.
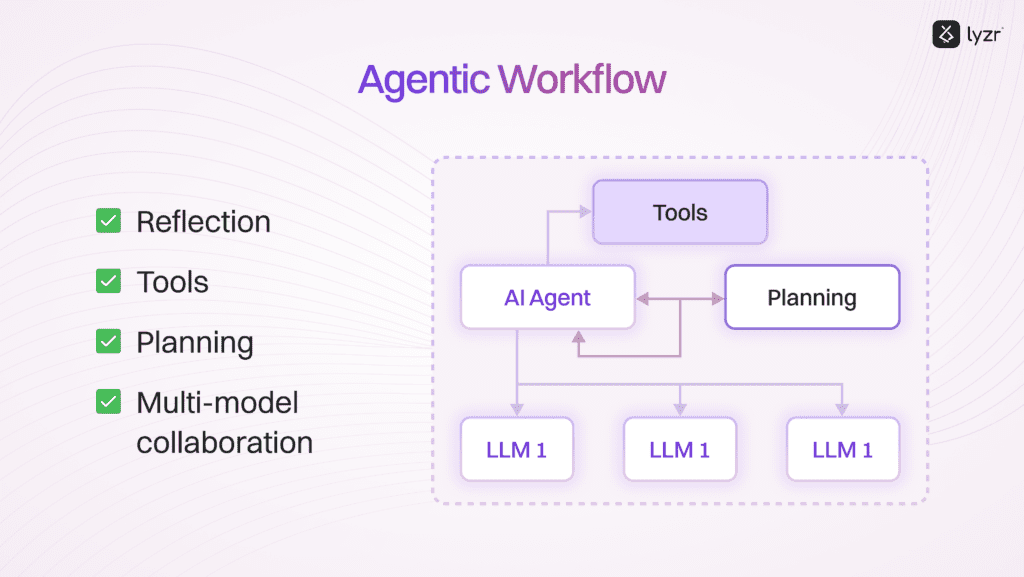
What is a Non Agentic System?
Non-agentic systems operate strictly within predefined rules and instructions. They require explicit commands for each action and cannot make independent decisions or adapt dynamically. These systems excel at handling straightforward, repetitive tasks but lack the flexibility to manage complex workflows without human intervention.
A Deep Dive into the Differences
Well because all the data points towards all workflows being agent led in the next decade.
The AI agent market was valued at ~$3.86 billion in 2023 & is projected to grow at a 45.1% CAGR from 2024 to 2030. (Refer: InfoWorld)
The global autonomous vehicle market is expected to grow from $1,921.1 billion in 2023 to $13,632.4 billion by 2030, exhibiting a CAGR of 32.3% during the forecast period.
And According to PwC, Generative AI, a subset of agentic AI, is poised to contribute between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion annually to global GDP by 2030 across various sectors.
And finally by 2025, it is projected that 70% of organizations will have operationalized AI architectures with agentic workflows playing a crucial role in this expansion.
Ok, since the data substantiates it, lets jump into the overall differences between agentic & non-agentic workflows
- Overall Differences
| Aspect | Agentic Systems 🤖 | Non-Agentic Systems 📱 | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | Acts solo, makes own choices | Needs human commands | AI assistant 🗓️ / Manual calendar |
| Adaptability | Learns and changes | Sticks to fixed rules | AI adapts 🔄 / Static software |
| Complex Tasks | Handles multi-step jobs | Does simple, single tasks | Autonomous drone 🚁 / Remote drone |
| Decision Making | Plans and decides goals | Follows set scripts | AI plans projects 📊 / Scripted bot |
Technical Architecture Differences
1. Agentic Systems Architecture (Complex)
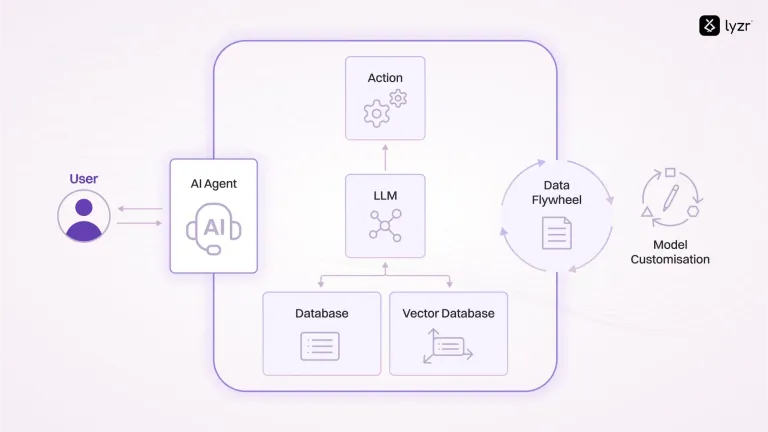
- Perception Module: Gathers data from the environment (Text, Camera, Audio, Sensors)
- Reasoning & Cognition Engine: Processes the perceived data to make informed decisions. Ex: Memory, Knowledge Base
- Action Module: Executes decisions by performing specific actions
- Learning Component: Enables the system to learn from experiences and adapt over time. Ex: Human Re-enforced Learning
- Communication Interface: Allows interaction with other systems or agents. (Voice/Text)
Agentic AI operates through four stages: Perceive, Reason, Act, and Learn, effectively managing complex tasks and showcasing its decision-making and problem-solving abilities.
Solves problems in four simple steps:
1: Perceive: First, AI agents collect data from all sorts of sources, like sensors, databases, and digital interfaces. They sift through this information to recognize important details, like objects or key entities.
2: Reason: Next, a large language model takes charge, understanding the task at hand and figuring out the best solution. It also coordinates specialized models for specific tasks, like creating content or making recommendations, using advanced methods like retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to tap into proprietary data for spot-on results.
3: Act: Once the plan is set, AI takes action. It integrates with tools and software to carry out tasks quickly and efficiently. Built-in guardrails help ensure everything’s done correctly. For instance, a customer service AI might process claims under a certain amount, but anything higher gets flagged for human approval.
4: Learn: Finally, the system gets smarter over time. Through a continuous feedback loop, the data from its actions feeds back into the system, helping it improve and adapt for even better decision-making and efficiency.
Example of an Agentic System: An AI-powered personal assistant that autonomously manages your schedule, emails, and reminders. It adapts to your preferences, learns from past interactions, and proactively suggests optimizations.
2. Non-Agentic Systems Architecture
Non-agentic systems operate based on predefined rules and require human input for decision-making. Their architecture generally comprises:
- Input Interface: Receives commands or data from users.
- Processing Unit: Executes predefined algorithms to process inputs.
- Output Interface: Delivers results based on processed data.
Example of a Non-Agentic System: A traditional chatbot that provides predefined responses to specific queries. It requires explicit user input for each interaction and cannot perform tasks beyond its programmed capabilities.
What are some of the other architectural differences?
| Aspect | Agentic Systems 🤖 | Non-Agentic Systems 📱 | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture Type | Modular and flexible for easy customization | Monolithic and rigid, hard to customize | Modular CRM with AI features 🔧 / Legacy CRM needing big changes |
| Workflow Logic | Separate from core logic, adaptable workflows | Built into core logic, rigid workflows | Workflows swapped easily 🔄 / Fixed workflows |
| Integration Capability | Adds features smoothly without disruption | New features disrupt or need workarounds | Add AI analytics smoothly 🤖 / Complex upgrades causing downtime |
| Modularity | Modular design enables easy feature add-ons | Requires major restructuring for new features | Modular CRM adding AI analytics 🧩 / Monolithic CRM needing overhaul |
What are the workflow differences?
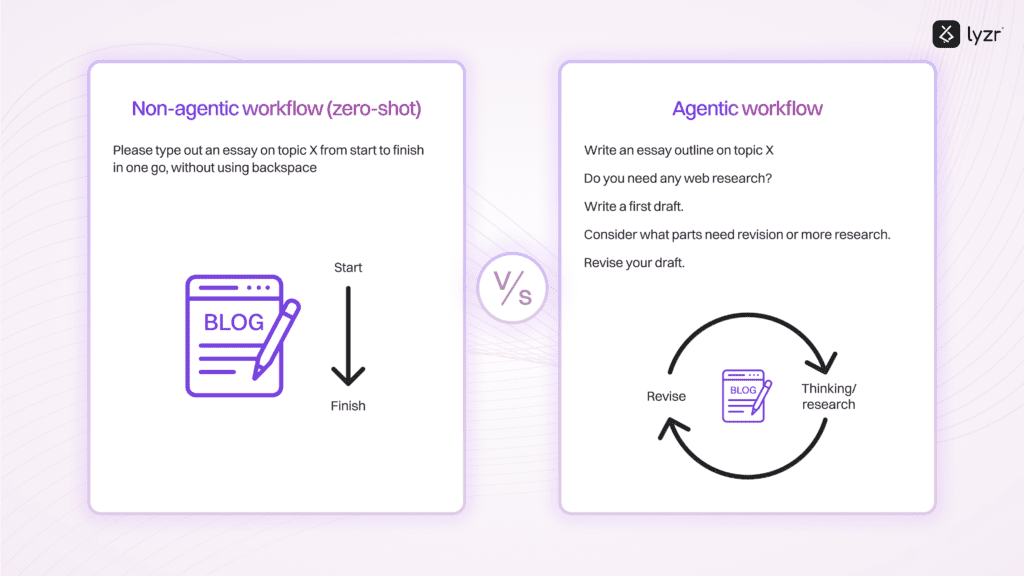
Connecting the Dots: Integration and Data Flow
The way systems integrate and share data has evolved, shaping how efficiently they work together. Early systems relied on siloed operations and manual data transfers, while modern approaches enable easier data flow and integration across platforms, driving smarter and more connected outcomes.
| Aspect | Agentic Systems | Non-Agentic Systems |
| Data Integration | Facilitate seamless cross-application and data integration by maintaining neutrality. Agentic System: An AI platform that consolidates data from various sources, providing real-time insights and recommendations. | Often operate in silos, making data integration across different applications challenging. Non-Agentic System: Separate databases requiring manual data extraction and analysis. |
| Ecosystem Collaboration | Allow users to work across ecosystems holistically, enhancing efficiency and collaboration. | Separation leads to inefficiencies and data inconsistencies. |
| Scalability | Easily scalable due to modular architecture and dynamic data flow. | Scalability is limited by rigid structures and isolated data systems. |
Examples of Agentic & Non-Agentic Workflows Across Industries
The evolution of workflows is increasingly characterized by the integration of agentic systems—autonomous agents capable of performing tasks with minimal human intervention.
As we have covered the differences, lets look at how it trickles into industries.
Here is a detailed comparison of non-agentic versus agentic workflows across multiple industries:
1. Healthcare → Patient Monitoring
Non-Agentic Workflow: Patients in a hospital are connected to static monitoring devices. Nurses manually record vitals (e.g., heart rate, blood pressure) every few hours. Critical anomalies between recordings may go unnoticed. Example: A patient’s blood pressure spikes at 2 AM, but it isn’t detected until the nurse’s 6 AM round.
Agentic Workflow: AI agents continuously monitor patient vitals in real-time, analyzing data for anomalies. When a critical issue arises, the system alerts the medical team and suggests immediate interventions. Example: The AI detects a patient’s rising blood pressure at 2 AM, alerts the nurse on duty, and recommends administering medication.
2. Transportation: Logistics Optimization
Non-Agentic Workflow: Delivery schedules are created using static maps and historical traffic data. If unexpected events like road closures occur, drivers must manually adjust their routes. Example: A delivery driver encounters heavy traffic and a closed road, delaying the shipment because the system lacks real-time adaptability.
Agentic Workflow: AI agents dynamically plan and adjust routes in real-time, considering current traffic, weather, and road conditions. They also optimize delivery schedules based on package priority and location. Example: The AI reroutes the delivery truck before the driver encounters traffic, ensuring timely shipment while optimizing fuel efficiency.
3. Sales and Marketing: Lead Generation
Non-Agentic Workflow: Lead Generation: Sales teams manually qualify leads by reviewing lists from static CRM systems. This process is time-consuming and prone to human error. Example: A salesperson calls 50 potential leads from a downloaded list, only to find that most are unqualified.
Agentic Workflow: AI agents analyze data to autonomously qualify and prioritize leads based on engagement, behavior, and predefined criteria. Agents also initiate personalized outreach. Example: The AI filters a list of 50 leads, prioritizing 10 with the highest likelihood of conversion, and sends tailored introductory emails to each.
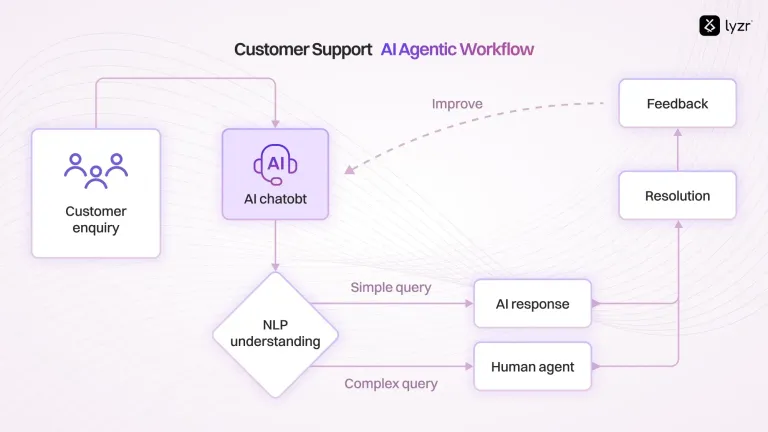
4. Customer Support: Issue Resolution
Agentic Workflow: AI agents manage complex customer issues by understanding context, processing refunds, and updating account details autonomously. Escalation is only required for exceptions.
Example: The AI processes the customer’s refund request, updates their account, and sends a confirmation email within minutes, requiring no human intervention.
5. Banking: Fraud Detection
Non-Agentic Workflow: Transactions exceeding a predefined threshold trigger a generic fraud alert. Customers must verify the transaction manually by contacting the bank. Example: A customer’s credit card purchase is flagged as fraudulent, requiring them to call the bank and verify the transaction.
Agentic Workflow: AI agents monitor transactions in real-time, analyzing spending patterns and context to determine fraud probability. They proactively notify customers and allow verification via voice or app. Example: The AI detects an unusual transaction, sends a notification to the customer, and verifies the purchase through a quick app interaction.
What are some of the most commonly asked questions?
1. How do agentic systems handle complex tasks compared to non-agentic systems?
Agentic systems are designed to autonomously manage complex, multi-step tasks by perceiving their environment, making decisions, and adapting to new information without human intervention. They can set goals, plan strategies, and execute actions independently. In contrast, non-agentic systems operate based on predefined rules and require human input for each step, limiting their ability to handle intricate tasks.
2. What are the implications of agentic systems on data privacy and security?
Agentic systems, due to their autonomous nature, often require access to vast amounts of data to function effectively. This raises concerns about data privacy and security, as these systems must handle sensitive information responsibly. Ensuring robust data encryption, compliance with privacy regulations, and implementing strict access controls are essential to mitigate potential risks. An agentic personal assistant that manages your emails, calendar, and financial transactions needs access to sensitive personal information, necessitating stringent security measures to protect your data.
3. What are the cost implications of implementing agentic systems compared to non-agentic systems?
Implementing agentic systems can involve higher initial costs due to their complexity and the advanced technology required. Non-agentic systems may have lower upfront costs but could incur higher operational expenses over time due to their limited automation capabilities.
4. How do agentic systems integrate with existing technology infrastructures compared to non-agentic systems?
Agentic systems are designed with flexibility in mind, allowing seamless integration into existing technology infrastructures. They can adapt to various platforms and workflows, often requiring minimal adjustments for compatibility.
For example, Lyzr’s agentic framework integrates with 200+ LLMs, tooling across all functions (Ex: Gmail,Calendar, Hubspot) and accepts all forms of input (video, audio and text) as RAG.
5. What are the ethical considerations when deploying agentic systems versus non-agentic systems?
Deploying agentic systems raises ethical considerations, including decision-making transparency, accountability, and potential biases in autonomous actions. Ensuring these systems operate within ethical guidelines and societal norms is crucial. Non-agentic systems, being more controlled and predictable, present fewer ethical dilemmas but still require oversight to prevent misuse.
6. What’s the main difference between agentic and non-agentic systems?
Agentic systems act independently and make decisions, while non-agentic systems rely on explicit human input and follow fixed instructions.
7. Can agentic systems handle complex tasks better?
Yes, agentic systems manage multi-step tasks on their own, unlike non-agentic systems which perform simple, single tasks controlled by users.
8. Are agentic systems easier to customize and upgrade?
Generally, yes. Agentic systems have modular architectures allowing smooth integration of new features, while non-agentic systems tend to be rigid and harder to modify.
Experience agentic AI that’s built to lead
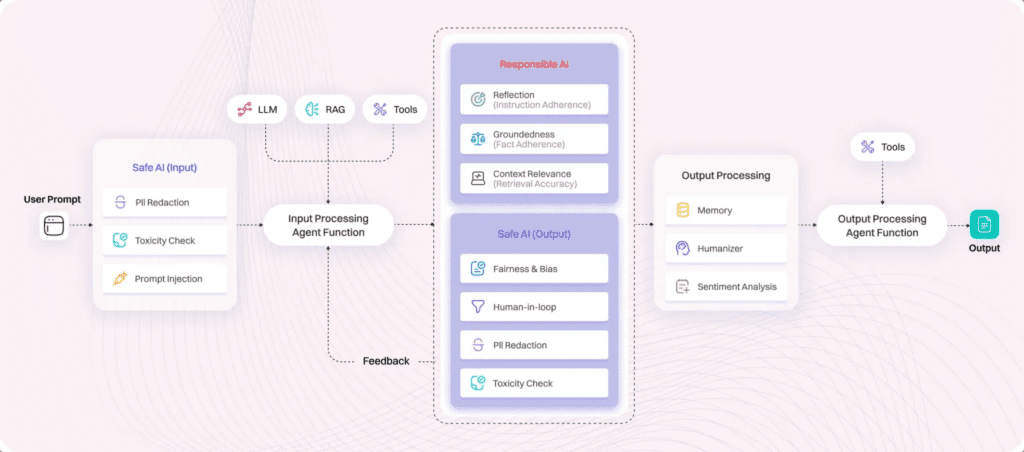
Well since agentic workflows are the future, if youre looking to explore agents & are looking to automate workflows, come speak to us at Lyzr.
We are happy to walk you through what is possible. And similarly if you’re looking to build on your own, do explore our pre-built agents on Lyzr Studio. We have quite a few for banking, sales, marketing, customer support and more.
Lyzr is trusted by builders and enterprise teamsread verified reviews on leading marketplaces
Book A Demo: Click Here
Join our Slack: Click Here
Link to our GitHub: Click Here